In this section some detection, defense tools and security advisors are going to be discussed.
Protect / Limit Domain Admins
It is recommended to protect and limit domain admins:
- Reduce the number of Domain Admins.
- Do not allow or limit the login of DAs to any other machine rather than the Domain Controllers. In case of need it, ensure that there are no other local machine on the target.
- Try to never run a service with a Domain Admin (Service Accounts passwords are stored in LSAS and no protections are setted).
- Set
Account is sensitive and cannot be delegatedfor Domain Admins.
Windows Defender
Microsoft Defender Antivirus is available in Windows 10 and Windows 11, and in versions of Windows Server.
Microsoft Defender Antivirus is a major component of your next-generation protection in Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. This protection brings together machine learning, big-data analysis, in-depth threat resistance research, and the Microsoft cloud infrastructure to protect devices (or endpoints) in your organization. Microsoft Defender Antivirus is built into Windows, and it works with Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to provide protection on your device and in the cloud.
It has three different modes:
-
Active mode: In active mode, Microsoft Defender Antivirus is used as the primary antivirus app on the device. Files are scanned, threats are remediated, and detected threats are listed in your organization’s security reports and in your Windows Security app.
-
Passive mode: In passive mode, Microsoft Defender Antivirus is not used as the primary antivirus app on the device. Files are scanned, and detected threats are reported, but threats are not remediated by Microsoft Defender Antivirus. IMPORTANT: Microsoft Defender Antivirus can run in passive mode only on endpoints that are onboarded to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint.
-
Disabled or uninstalled: When disabled or uninstalled, Microsoft Defender Antivirus is not used. Files are not scanned, and threats are not remediated. In general, we do not recommend disabling or uninstalling Microsoft Defender Antivirus.
More info in:
LSA Protection
In Windows 8.1 and later microsoft has provided addition protection for the LSA to prevent untrusted processes from being able to read its memory or inject code. This will prevent mimikatz sekurlsa::logonpasswords for working properly.
To activate this protection set to 1 the value of RunAsPPL:
reg query HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\LSA /v RunAsPPL
reg add HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\LSA /v RunAsPPL /t REG_DWORD /d 1
This LSA protection can be bypass using mimikatz mimidrv.sys driver:
mimikatz # !+
mimikatz # !processprotect /process:lsass.exe /remove
Disable WDigest
Windows Digest (WDigest) is a authentication protocol introduced in Windows XP and was designed to be used with HTTP protocol which means that plain-text passwords are stored in the LSASS.
Invoke-Mimikatz -Command '"sekurlsa::wdigest"'
This behaviour can be disabled via registry setting to 1 the value of UseLogonCredential and Negotiate
reg query HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\WDigest /v UseLogonCredential
reg add HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\WDigest /v UseLogonCredential /t REG_DWORD /d 1
reg add HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\WDigest /v Negotiate /t REG_DWORD /d 1
Note: Microsoft has this protocol enabled by default in Windows XP, Windows 8.0, Windows Server 2003 and Windows Server 2012.
LAPS
LAPS (Local Administrator Password Solution) is a centralized storage of passwords for local administrator in active directory with a periodic randomizing where read permissions are access controlled. Computer objects where LAPS is activated has two new attributes:
-
ms-mcs-AdmPwdattribute stores the clear text pasword. -
ms-mcs-AdmPwdExpitarionTimecontrols the password change.
Although the password is stored in clear text, te transmission is encrypted. With careful enumeration, it is possible to retrieve which users can access the clear text password providing a list of attractive targets.
More info in:
Credential Guard
Credential Guard or Windows Defender Credential Guard is a new feature in Windows 10 Entreprise and Education edition and Windows Server 2016 that helps to protect your credentials on a machine from threats such as PassTheHash or Over-PassTheHash by restricting access to NTLM hashes and TGTs.
It uses virtualization based security to isolate secrets so that only privileges system software can access them. Credential Guard must be turned on and deployed in your organization as it is not enabled by default.
Since it is activated it is no posible to access the secrets in LSASS.
Note: During the PassTheHash technique we write on LSASS.
To check if Credential Guard is enabled check the following registry:
reg query HKLM\System\CurrentControlSet\Control\LSA /v LsaCfgFlags
Credential Guard could be enabled in different ways:
| Value | Mode |
|---|---|
| 0 | Disabled |
| 1 | Enabled with UEFI lock |
| 2 | Enabled without UEFI lock |
Credentials for local accounts in SAM and Service Account Credentials from LSA Secrets are not protected.
BlueTeam Note: Credential Guard cannot be enabled on a DC because it breaks the authentication.
More info in:
AppLocker
AppLocker is a Windows Defender functionallity which helps you control which apps and files users can run. These include executable files, scripts, Windows Installer files, dynamic-link libraries (DLLs), packaged apps, and packaged app installers.
AppLocker can help you:
- Define rules based on file attributes that persist across app updates, such as the publisher name (derived from the digital signature), product name, file name, and file version. You can also create rules based on the file path and hash.
- Assign a rule to a security group or an individual user.
- Create exceptions to rules. For example, you can create a rule that allows all users to run all Windows binaries, except the Registry Editor (regedit.exe).
- Use audit-only mode to deploy the policy and understand its impact before enforcing it.
- Create rules on a staging server, test them, then export them to your production environment and import them into a Group Policy Object.
- Simplify creating and managing AppLocker rules by using Windows PowerShell.
Powershell 5.1
Upgrade to Windows PowerShell 5.1, this offers multiple security controls which certainly increase the costs to attacker.
Whitelisting
Use Application Control Policies (Applocker) and Device Guard to restrict PowerShell scripts. If Applocker is configured in “Allow mode” for scripts, Powershell 5 automatically uses the Constrained Language Mode.
Bypass Whitelisting
If PowerShell is blocked, .NET code can use System.Management.Automation NameSpace to load PowerShell functionality.
C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\Framework\v4.0.30319>msbuild.exe pshell.xml
Enhanced Logging
Enhanced Logging allows BlueTeams to have a very in-depth look of an attacker’s activities if he is using PowerShell.
Warning level script block logging only for a known list of suspicious commands. A large number of logs for script block logging is created. Even more if invocation of script blocks is logged.
A huge number of logs when module logging is enabled.
Script Block Logging
Set EnableSciptBlockLogging to 1 in the following registry:
HKLM:\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\ScriptBlockLogging
PowerShell v5 onwards logs (Warning level Event ID 4104) some suspicious script blocks automatically based on a list of suspicious commands.
It also records the original obfuscated code as well decoded and deobfuscated code.
Module Logging
Available since PowerShell v3, module logging logs pipeline execution and command execution events.
Can be enabled using GPO, use * to log all modules:
Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Windows PowerShell -> Turn on Module Logging
We can also modify the registry. Set EnableModuleLogging to 1:
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\ModuleLogging
And create a key * and set it to * for all modules.
HKLM\SOFTWARE\Wow6432Node\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\ModuleLogging\ModuleNames
Bypass Script Block Logging
Script Block logging can be bypassed on the current session without admin rights by disabing it from the Group Policy Cache.
$GroupPolicyField=[ref].Assembly.GetType('System.Management.Automation.Utils')."GetFie`ld"('cachedGroupPolicySettings','N'+'onPublic,Static')If($GroupPolicyField) {$GroupPolicyCache=$GroupPolicyField.GetValue($null)If($GroupPolicyCache['ScriptB'+'lockLogging']) {$GroupPolicyCache['ScriptB'+'lockLogging']['EnableScriptB'+'lockLogging']=0$GroupPolicyCache['ScriptB'+'lockLogging']['EnableScriptBlockInvocationLogging']=0}$val=[System.Collections.Generic.Dictionary[string,System.Object]]::new()$val.Add('EnableScriptB'+'lockLogging',0)$val.Add('EnableScriptB'+'lockInvocationLogging',0)$GroupPolicyCache['HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\ScriptB'+'lockLogging']=$val}
Unload Warning Level Script Block Logging
Recall that the Warning level script block logging which is enabled by default uses a lis of known bad words.
Turns out the logging can be bypassed for the current session without admin rights by setting the list of signatures field in the ScriptBlock class to null.
# The bypass
[ScriptBlock]."GetFiel`d"('signatures','N'+'onPublic,Static').SetValue($null,(New-ObjectCollections.Generic.HashSet[string]))
# To use a base64 encoded payload script with the bypass
[ScriptBlock]."GetFiel`d"('signatures','N'+'onPublic,Static').SetValue($null,(New-ObjectCollections.Generic.HashSet[string]));[Text.Encoding]::Unicode.GetString([Convert]::FromBase64String('IgA8AE0AeQAgAHMAdQBzAHAAaQBjAGkAbwB1AHMAIABOAG8AbgBQAHUAYgBsAGkAYwAgAHAAYQB5AGwAbwBhAGQAPgAiAA=='))|iex
System-Wide Transcription
Enables transciption (console logging) for everything which uses PowerShell engine such as powershell.exe, PowerShell ISE, custom hosts, .NET dll, msbuild, installutil, etc…
Can be enabled using Group Policy (GPO). By default transcripts are saved in the user’s “My Documents” directory.
Administrative Templates -> Windows Components -> Windows Powershell -> Turn on PowerShell Transcription
Set EnableTranscripting to 1 in the following registry:
HKLM:\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\PowerShell\Transcription
The transcripts are written as text files and can quicly grow in size because the command output is also recorded. It is always recommended to forward the transcirpts to a log system to avoid tampering and running out of disk space.
Note: Too many logs in an enterprise level network. Enabling Transcripts on a DC breaks the Active Directory Administartrion Centre GUI application.
AMSI
AMSI (AntiMalware Scan Interface) provides the registered antivirus access to contents of a script before execution.
This allows detection of malicious scripts regardless of input method such as disk, encodedcommand, in-memory.
Enabled by-default on Windows 10 and supported by Windows Defender.
Note: AMSI has no detection mechanism. It is dependent on the signature based detection by the registered antivirus.
Constrained Language
Language mode in PoweShell is used to control access to different elements for a PowerShell session.
In the constrained language mode, all Windows cmdlets and elements are allowed but allows only limited types. For examples, Add-Type, Win32APIs, COM objects are not allowed.
Intended to work with Applocker in Allow mode or UMCI (Device Guard User Mode Code Integrity). When Allow mode is set for scripts in Applocker, the Constrained Language mode kicks-in by itself.
Note: Not easy to implement enterprise-wide.
JEA (Just Enough Administration)
JEA (Just Enough Administration) provides role based access control for PowerShell based remote delegated administration. With JEA non-admin users can connect remotely to machines for doing specific tasks.
Focused more on securing privileged access than solving a problem introduced with PowerShell unlike others discussed for far.
JEA endpoints have PowerShell transcription and logging enabled.
Device Guard
Device Guard or Windows Defender Device Guard is a group of features designed to harden a system agains malware attacks. Its focus in preventing malicious code from running by ensuring only known good code can run.
Has three main components:
- Configurable Code Integrity (CCI): Configure only trusted code to run.
- Virtual Secure Mode Protected Code Integrity: Enforces CCI with Kernel Mode (KMCI) and User Mode (UMCI).
- Platform and UEFI Secure Boot: Ensures boot binaries and firmware integrity.
UMCI is something which interferes with most of the lateral movement attacks we have seen. While it depends on the deployment, many well known applications are whitelisted such as csc.exe, msbuild.exe, etc…
More info in:
Protected Users Group
Protected Users is a gorup introcued in Server 2012 R2 for better protection against credential theft. Credentials of all members of the the protected users group are not cached in a insecure way. A user added to this group:
- Members cannot use
CredSSPorWDigestfor authentication so no more cleartext credentials caching. - The NTLM hash will not cache the user’s plain text credentials or NT one-way function (NTOWF).
- Kerberos does not use DES or RCE4 keys. No caching of clear text credentials or long term keys after the initial TGT is acquired.
- A cached verifier is not created at sig-in or unlock, so offline sign-in is no longer supported.
If the domain functional level is Server 2012 R2:
- No NTLM authentication.
- No DES or RC4 keys in Kerberos pre-auth.
- No delegation (constrained or unconstrained).
- No renewal of TGT beyond initial for hour lifetime. Hardcoded, unconfigurable Maximum lifetime for use ticket and Maximum lifetime for user ticket renewal.
Protected accounts and groups in active directory by operating system:
| User/Group | Windows Server 2003 RTM | Windows Server 2003 SP1+ | Windows Server 2012, Windows Server 2008 R2, Windows Server 2008 | Windows Server 2016 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Account Operators | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Administrator | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Administrators | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Backup Operators | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Cert Publishers | ✓ | × | × | × |
| Domain Admins | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Domain Controllers | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Enterprise Admins | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Krbtgt | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Print Operators | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Read-only Domain Controllers | × | × | ✓ | ✓ |
| Replicator | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Schema Admins | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| Server Operators | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
- BlueTeam Note: Microsoft do not recommend to add
Domain AdminsorEnterprise Adminsto this group without testing the potential impact of lock out.
More info in:
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/security/credentials-protection-and-management/protected-users-security-group
- https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/windows-server/identity/ad-ds/plan/security-best-practices/appendix-c–protected-accounts-and-groups-in-active-directory
Use of Privileged Administrative Workstations (PAWs)
If the user of the IT department which is a Domain Admin is compromised, in that case there is a risk for the infraestructure and the active directory. For that reason the administrator needs to have aparate hardened workstation to permorm sensitive tasks like administration of domain controllers, cloud infraestructure, sensistive business functions etc…
This can provide protection from phishing attacks, OS vulnerabilities, credential replay attacks, etc…
Admin jump servers should be configured to be accessed only from a PAW. We can apply different strategies:
- Separate privilege and hardware for administrative and normal tasks.
- Having a VM on a PAW for user tasks.
AD Administrative Tier Model
The Active Directory Administrative Tier Model is composed of three levels only for administrative accounts:
- Tier 1: Accoutns, groups and computers which have privileges across athe enterprise like domain controllers, domain admins, entreprise admins.
- Tier 2: Accounts, groups and computers which have access to resources having significant amount of business value. A common example role is server administrators who maintain these operating systems with the ability to impact all enterprise servers.
- Tier 3: Administrator accounts which have administrative control of a significant amount of business value that is hosted on user workstations and devices. Examples include Help Desk and computer support administrators because can impact the integrity of almost any user data.
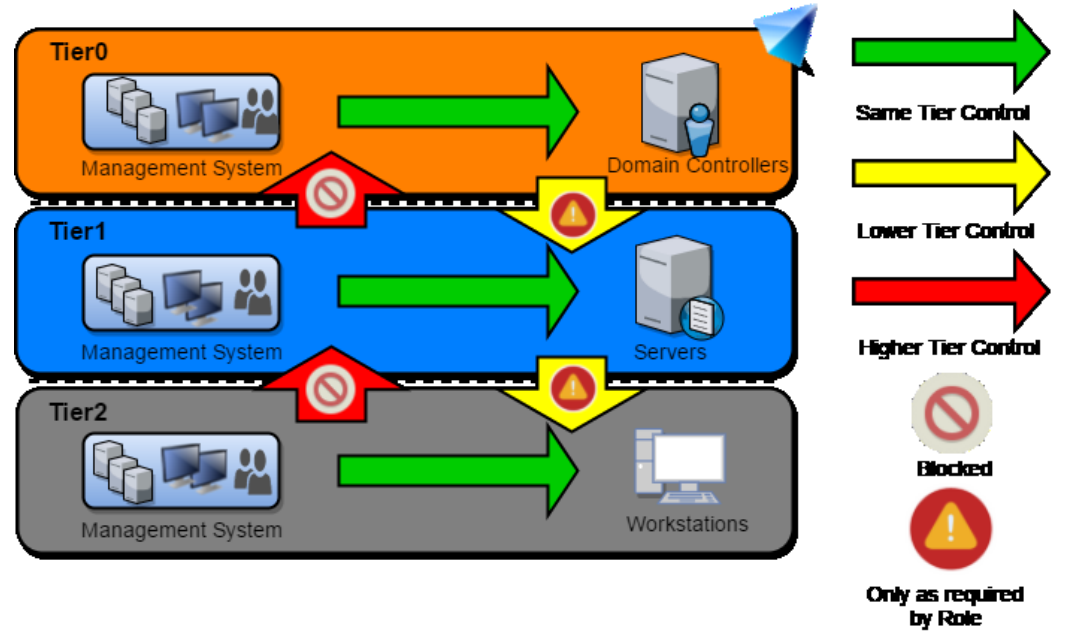
Control Restrictions
Control restrictions is what admins can control.
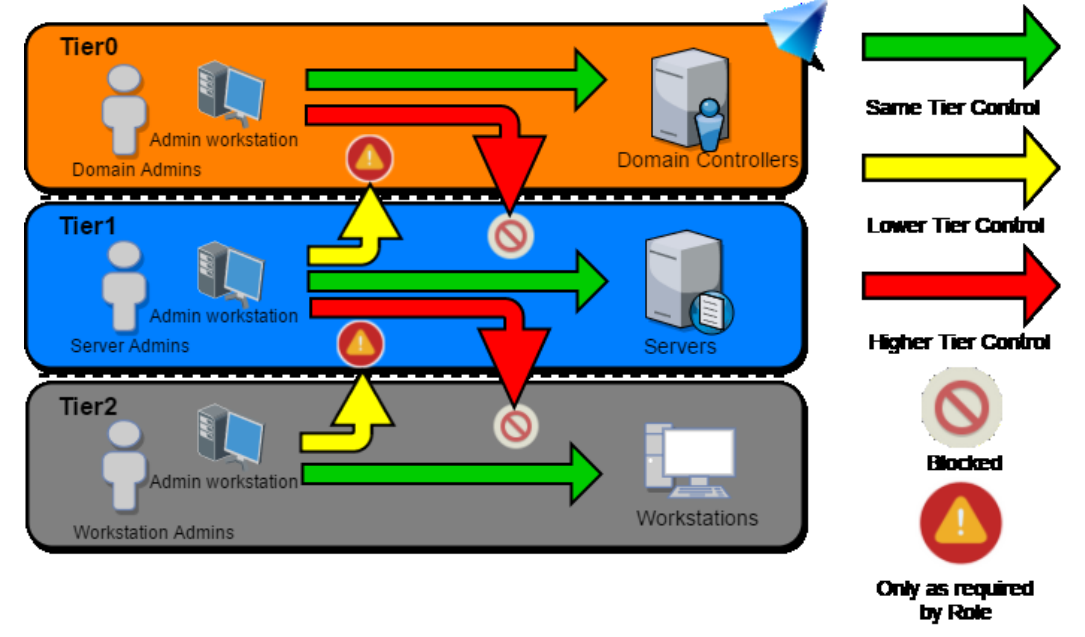
Logon Restrictions
Logon restrictions is where admins can logon.
Enhanced Security Admin Environment (ESAE)
Enhanced Security Admin Environment (ESAE) is a dedicated administrative fores for managing critical assets like administrative users, groups and computers. Since a forest is considered a security boundary rather than a domain, this model provides enhanced security controls.
The amdinistrative forest is also called the Red Forest. Administrative users in a production forest are used as standard non-privileged users in the administrative forest.
Selective authentication to the Red Forest enables stricter security controls and logon of users from non-administrative forests.
 Hacking Notes
Hacking Notes