It’s an introduction of hacking WiFi, I recollected from the community including others blogs for my own and guides to pass OSWP certificate.
Hardware required:
An antena that could configure to monitor mode:
- AWUS036ACH: Wide range 2.4GHz/5GHz
Software required:
There are some linux distributions like wifislax that could be useful to us, but I used Parrot OS distribution and Kali Linux which have almost all the programs used in that notes, if not install it with apk install
- aircrack-ng suite
- hostapd-wpe
- hashcat
- JohnTheRipper
- mdk3
- tshark
- pyrit
- hccap2john
- genpmk
- mysql
- bettercap
- hcxdumptool
- WPSPinGenerator
- macchanger
Introduction
Wi-Fi allows networking of computers and digital devices without the need for wires. Data is transferred over radio frequencies, allowing Wi-Fi capable devices to receive and transmit data when they are in range of a Wi-Fi network.
Wi-Fi uses a radio technology known as 802.11, which can transmit data over short distances using high frequencies. 802.11 operates on either 2.4GHz or 5GHz depending on its type.
To understand how to attack WLAN, we need first to understand how it works. Take a look in detail from networking basis.
OSI Model
The OSI Model (Open Systems Interconnection Model) is a conceptual framework used to describe the functions of a networking system.
The OSI model characterizes computing functions into a universal set of rules and requirements in order to support interoperability between different products and software. In the OSI reference model, the communications between a computing system are split into seven different abstraction layers: Physical, Data Link, Network, Transport, Session, Presentation, and Application.
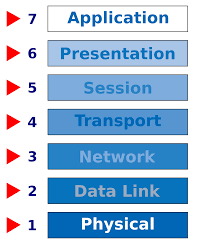
We are going to see Physical Layer and deep on Data link Layer.
Physical Layer
The physical layer is the lowest layer of the OSI Model and is concerned about how it is transmitted, via electricity, via optical or via radiofrecuence. Contain raw unstructured data bits across the network from the physical layer of the sending device to the physical layer receiving device. In case of WiFi it is transmitted via radiofrecuence.
Data Link Layer
At the data link layer, directly connected nodes are used to perform node-to-node data transfer where data is packaged into frames. The data link layer corrects error that may have occurred at the physical layer.
Its main functions are Data Link Control and Multiple Access Control.
Data Link Control
The Data Link Control is responsible for reliable transmissions of messages over transmission channel by using techniques like framing, error control and flow control. For Data Link Control refer to Stop and Wait ARQ.
Stop and Wait ARQ is a protocol that consist of send a packet and stop sending until we received a confirmation of received or acknowledge (ACK).
Multiple Access Control
If there is a dedicated link between the sender and the receiver such as a Ethernet wire between two devices then data link control is sufficient, however if there is no dedicated link present then multiple stations can access the channel simultaneously which is the case of Wi-Fi, where all clients try to send in the same medium (air).
Then multiple access protocols are required to decrease collisions and avoid cross-talk. Multiple access protocols are divided in:
Random Access Protocols
In these types of protocols, all stations have the same priority and any station can send data depending on medium’s state, idle or busy.
It has two features:
- There is no fixed time for sending data
- There is no fixed sequence of stations sending data
ALOHA, CSMA, CSMA/CD and CSMA/CA are random access protocols.
Controlled Access Protocols
In these types of protocols, the data is sent by a selection which is approved by all other stations. Here appears the significant of “Token”.
Reservation, Polling and Token Passing are some of the controlled access protocols.
Channelization Protocols
Finally, the last type are channelization protocols, where the available bandwidth of the link is shared in time, frequency and code to multiple stations to access channel simultaneously.
- Frequency Division Multiple Access (FDMA), where the available bandwidth is divided into equals slots so each station can be allocated in its own band.
- Time Division Multiple Access (TDMA), has the same logic like FDMA but here the time is divided in slots instead of frequency.
- Code Division Multiple Access (CDMA) where one channel carries all transmissions simultaneously. There is neither division of bandwidth nor division of time. All transmission uses different codes.
Introduction to CSMA/CA
This method was developed to decrease the chances of collisions when two or more stations start sending their signals over the data-link layer. Carrier Sense multiple Access requires that each station check the state of the medium before sending. This protocol is used in 802.11 (WLAN).
The basic idea behind CSMA/CA is that the station should be able to receive while transmitting to detect a collision from different stations. In wired networks, if a collision occurs then the energy of received signal almost doubles and the station can sense the possibility of collision. In case of wireless networks, most of the energy is used for transmission and the energy of received signal increases by only 5-10% if a collision occurs so it can not be used by the station to sense collision.
Therefore CSMA/CA has been specially designed for wireless networks because will try to avoid these collisions.
There are three types of strategies:
- InterFrame Space (IFS): When a station finds the channel busy, it waits for a period of time called IFS time. Also can be used to define a priority, if the IFS is higher IFS then the priority decrease.
- Contention Windows: It is the amount of time divided into slots. A station which is ready to send frames chooses random number of slots as wait time.
- Acknowledgements: The positive acknowledgements and time-out timer can help to guarantee a successful transmission of the frame.
802.11 Frame Types and Formats
There are three types of 802.11 frames, which are management, control and data.
Management Frames
Management frames are used to manage the base station. This includes probing, associating, roaming and disconnecting clients from the base station.
- Association Request / Response: Stations send association requests to access points (APs) requesting to join the base station or BSS. The AP responds to the station using an association response frame that includes an association ID (AID). Each station within the BSS has a unique AID.
- Reassociation Request / Response: Stations send reassociation request to APs that wish to roam to. The AP responds to the station the same way it does in the association request/response. The primary difference between reassociation and association requests it that the station will indicate the current AP it is connected to in reassociation requests. The concept of roaming is to change of AP without loosing connection. (Remember that change AP doesn’t mind change network, maybe a office have a different AP in every floor, each one connected to same router).
- Probe Request / Response: As part of the active and passive scanning processes, stations send probe requests with a specific SSID, wildcard or null value in the SSID field to search for wireless networks. When the field is wildcard or null, the client is requesting any AP nearby to respond with all SSIDs using a probe response frame. When the probe request contains a specific SSID, the client is requesting any AP nearby to respond if they support that SSID. The probe response frame is a targeted beacon that is sent to the station who is “probing”.
- Beacon: APs send beacons at a regular interval called the target beacon transmit time (TBTT) to advertise the SSIDs they service. Beacons contain the configuration of the WLAN including whether it supports standards, required cipher and authentication key management methods, protection mechanisms etc.
- Authentication: Authentication frames are used to join the BSS as part of the open system authentication process. Open system authentication is a simple process used to verify that the station attempting to join the BSS has the capabilities to do so. The station sends an authentication request and the AP sends an authentication response.
- Dissasociation: A type of management frame sent from either the station or the AP. Disassociation frames are used to terminate the stations associations, it is a notification and does not expect a response. APs may disassociate clients for various reasons including failure to properly authenticate, for load balancing or timeout reasons, entering a state of maintenance, etc.
- Deauthentication: Deauthentication frames are used to reset the state machine for an associated client. The authentication process takes place prior to association therefor, if a station is deauthenticated, it is also disassociated. Deauthentication frames also include a reason code in the body of the frame from the table mentioned above.
- Action: Action frames are management frames that trigger an action to happen. The list of management frame sub types had become exhausted, so instead of creating new management frames as new technologies required them, the action frame can be used. Action frames do not expect an ACK.
- Timing Advertisement: Timing advertisement frames were introduced in 802.11p-2010; this standard describes how Wi-Fi can be used in vehicular environments. This type of management frame is not in use today and is expected to be used to communicate time values to devices that cannot maintain their own timing.
Control Frames
Control frames are used to control access to the medium and are used for frame acknowledgement.
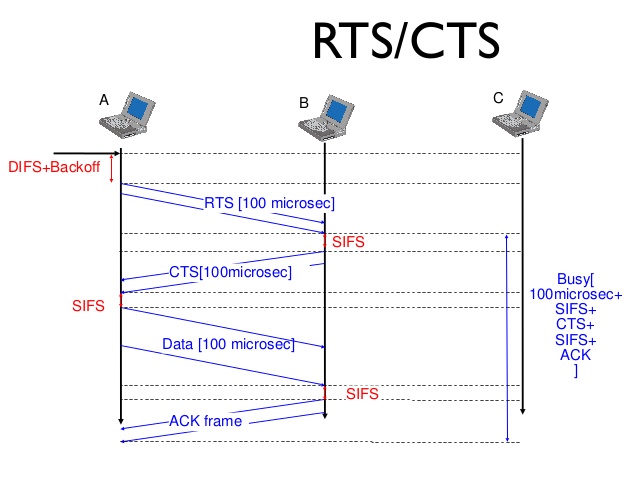
- Request to Send - RTS: Stations send RTS frames to reserve the medium for the amount of time, in microseconds, found in the duration field in the frame header. The medium will not be reserved for the station until it receives a clear to send frame response from the access point.
- Clear to Send - CTS: Frame sent by an AP in response to an RTS. CTS messages are sent at the lowest mandatory data rate, allowing them to reach all stations in the BSS. They only use the receiver address (RA) field in the header so the station in the receiver address field is the one that will be transmitting frames.
- Acknowledgement - ACK: ACK frames create a delivery verification method, they are expected after the transmission of data frames to confirm receipt of the frame. If the CRC check fails, the receiver will not send an ACK and if the sender does not receive an ACK, it will retransmit the frame.
- PS-Poll: PS-Poll frames are used to power save method to requests framed buffered on the AP while the client was sleeping.
- Block ACK / Block ACK Request: Block acknowledgement are used to confirm receipt of a block of QoS data frames.
- Beamforming Report Poll: Beamforming report poll frames are sent from the beamformer (the AP) to beamformees (STAs) to request additional feedback about the RF conditions.
- VHT/HE NDP Announcement: Null data packet (NDP) announcement frames notify the recipient that an NDP will follow.
Wi-Fi Attacks
Now that we look how Wi-Fi is working we will try to attack it. Exists some differents attacks to do in Wi-Fi environments:
- Rogue Wireless Devices: Create a backdoor to the network installing a AP on a device.
- Peer-to-peer Attacks: Attack other devices connected to the same AP.
- Eavesdropping: Monitor wireless communications.
- Encryption Cracking: Try to crack the encryption on the network. (WEP technologies)
- Authentication Attacks: Scrap a frame exchange between a client authenticating with the network and then they simply try to run an offline dictionary attack.
- MAC Spoofing: Change MAC address in order to bypass mac filters on the AP.
- Management Interface Exploits: Exploit panel admins of the AP or routers exposed to internet. (Default login)
- Wireless Hijacking: Configure a Evil Twin using the same ESSID as a public hotspot.
- Denial of Service: Try to modify the availability of the AP.
Now that we look how Wi-Fi works we will try to attack it.
References:
- https://blog.ct-networks.io/types-of-wireless-attacks-9b6ecc3317b9
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/carrier-sense-multiple-access-csma/
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/multiple-access-protocols-in-computer-network/
- https://www.ionos.com/digitalguide/server/know-how/csmaca-carrier-sense-multiple-access-with-collision-avoidance/
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/stop-and-wait-arq/
- https://howiwifi.com/2020/07/13/802-11-frame-types-and-formats/#:~:text=There are three types of,the layer 3%2D7 information.
- https://gist.github.com/s4vitar/3b42532d7d78bafc824fb28a95c8a5eb
- https://rootsh3ll.com/evil-twin-attack/
 Hacking Notes
Hacking Notes